10 Gbps E-band Mesh Network for Urban-Scale Projects
Forget expensive and time-consuming fiber installation.
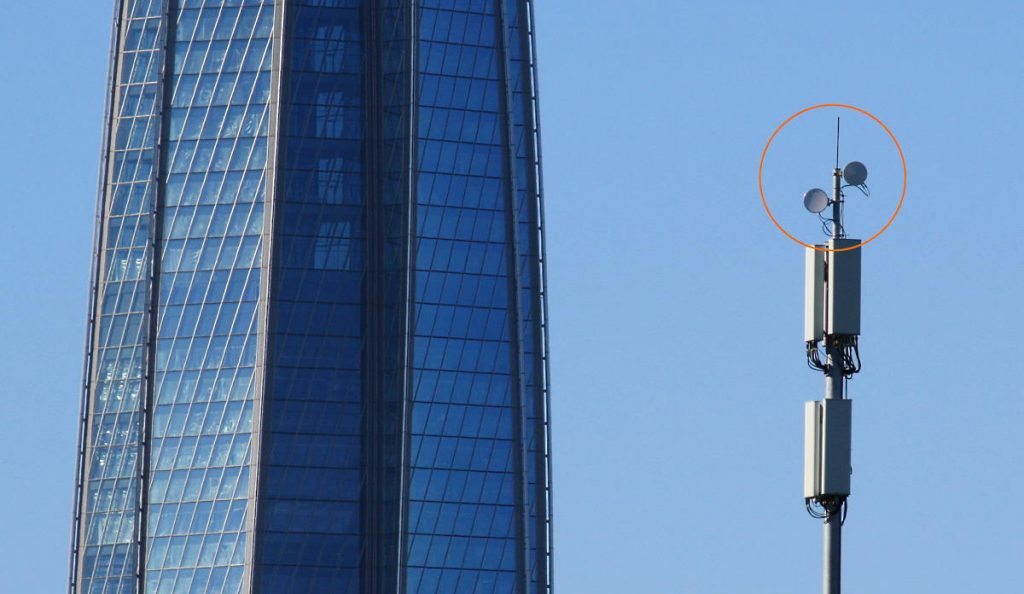
10 Gbps PPC-10G radios are the backbone of the city-scale E-band mesh network.
As our cities become increasingly connected, the need for reliable and high-speed wireless data networks increases.
With the E-band mesh network, high-speed wireless data transmission can be provided
covering all urban areas. Each node of the mesh network is equipped with a Linux edge
router that provides connectivity to the public Internet and a host of IP services required in
an urban environment.
What is 10 Gbps E-band mesh network
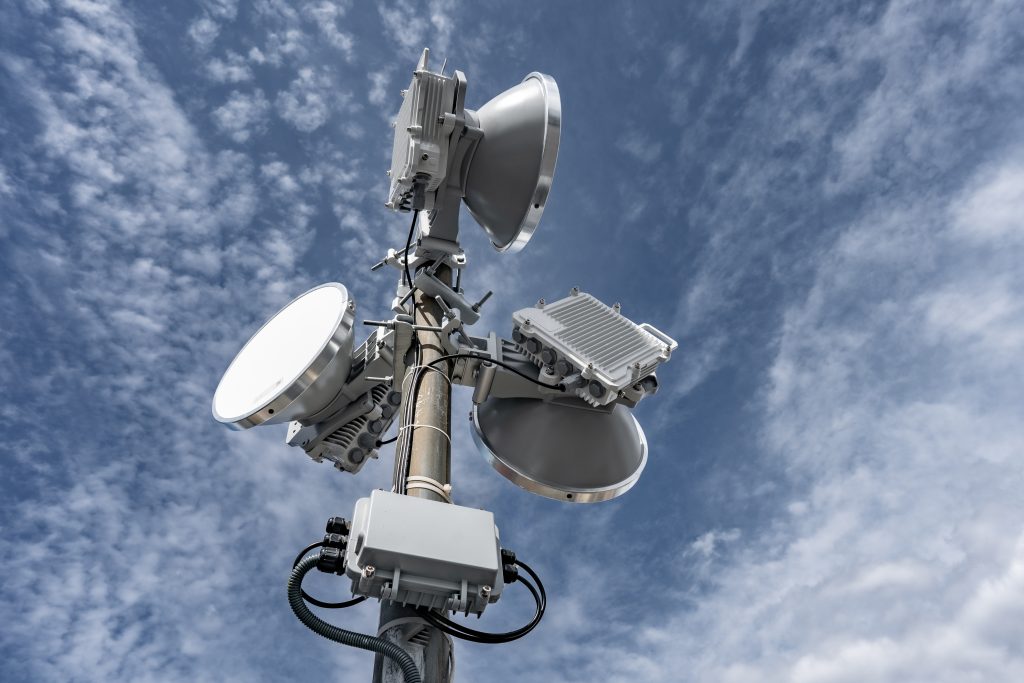
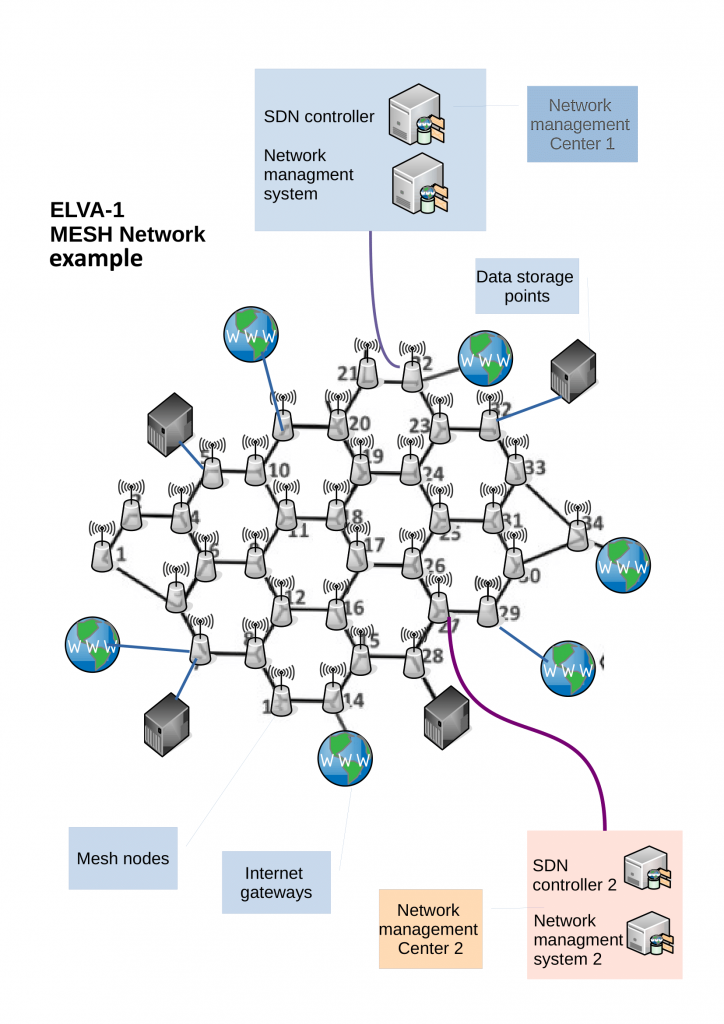
The wireless mesh network is intended to replace or back up 40- or 100-gigabit fiber rings and radials at the city scale. The ELVA-proposed mesh network operates at 70-80 GHz (E-band) and has a hexagonal topology with sides ranging from 1 to 5 km. Each mesh node has three 10 Gbit/s radiolinks (optional 20-40 Gbit/s) operating in full duplex mode. In this topology, each node has three (or more) 10 Gbps wireless links to neighboring nodes as well as the ability to connect to the operator’s fiber optic network for traffic exchange (if available in that location).
Using a wireless mesh network in cities of various size, it is possible to quickly deploy Smart City projects with video surveillance systems, face recognition, traffic control systems and Internet of Things (various sensors, gas analyzers, ticket machines for transport), and a multi-gigabit Internet connection to apartment blocks, business centers, industrial areas. For the areas of historic buildings equipment at 70-80 GHz in combination with 10-gigabit “last mile” radio links at 60 GHz allows to build home networks without the use of ugly fiber cables from rooftop to rooftop.
Traffic is automatically distributed across the mesh network nodes, finding optimal routes using advanced routing algorithms. In particular, there is no need to reconfigure network equipment (routers, switches, servers) when adding a new node.
Decentralized wireless mesh networks are resilient to the failure of any elements in the network and have multiple alternative routes for traffic, with node connectivity automatically ensured along the best route with dynamic realignment in case of channel bandwidth changes.
The emergence of new nodes increases network capacity because of new routes for traffic – each link runs at 10 Gbit/s (optional 20 – 40 Gbit/s). The total network capacity is determined by the number of alternative routes from one network node to another, reaching a total of 100 Gbit/s or more.
Each node uses an edge 10GE router (Edge-router) managed by on open-source software. This is a type of router located at the edge of the network and designed to provide connectivity between the user network (apartment building, video surveillance node, etc.) and the backbone mesh network. The router is developed on the basis of Linux, has 10-gigabit optical ports from radiolinks and output to the served user local network, has low power consumption with passive cooling and possibility of remote administration.
The ELVA-1 company emphasizes the difference of this technology from inexpensive analogues on Wi-Gig or Wi-Fi with half-duplex protocols of 802.хх family. PPC-10G-E radiolinks are full-duplex, – thus, each link is capable of transmitting traffic at 10 Gbps in both directions. In comparison, Wi-Fi or Wi-Gig technologies are half-duplex and the capacity of such 802.хх links will be distributed between Up-link and Down-link directions.
White Paper about ELVA-1 E-band Mesh Network Concept
For customers, wanted to know more about wireless backhaul mesh networking, ELVA-1 unveiled a white paper for a 10 Gbps E-band mesh network based on PPC-10G-E radio links and Linux-based 10GE edge routers.
Urban-scale E-band mesh networks from ELVA-1 offer a great solution to build an IP network over urban area, providing 10 to 40 Gbps wireless data connectivity in the 70-80 GHz frequency spectrum.
Download ELVA-1 “E-band 10 Gbps Urban-Scale Mesh Network White Paper” for more detail.
A mesh network is made up of many peer-to-peer nodes that are interconnected with each other. Each node in a mesh network has an edge router with a network management feature, meaning traffic can be automatically distributed across the network nodes by algorithmically finding optimal routes.