Introducing the Enhanced 10 Gbps MobiBridge-10G Black Edition Radio Link by ELVA-1
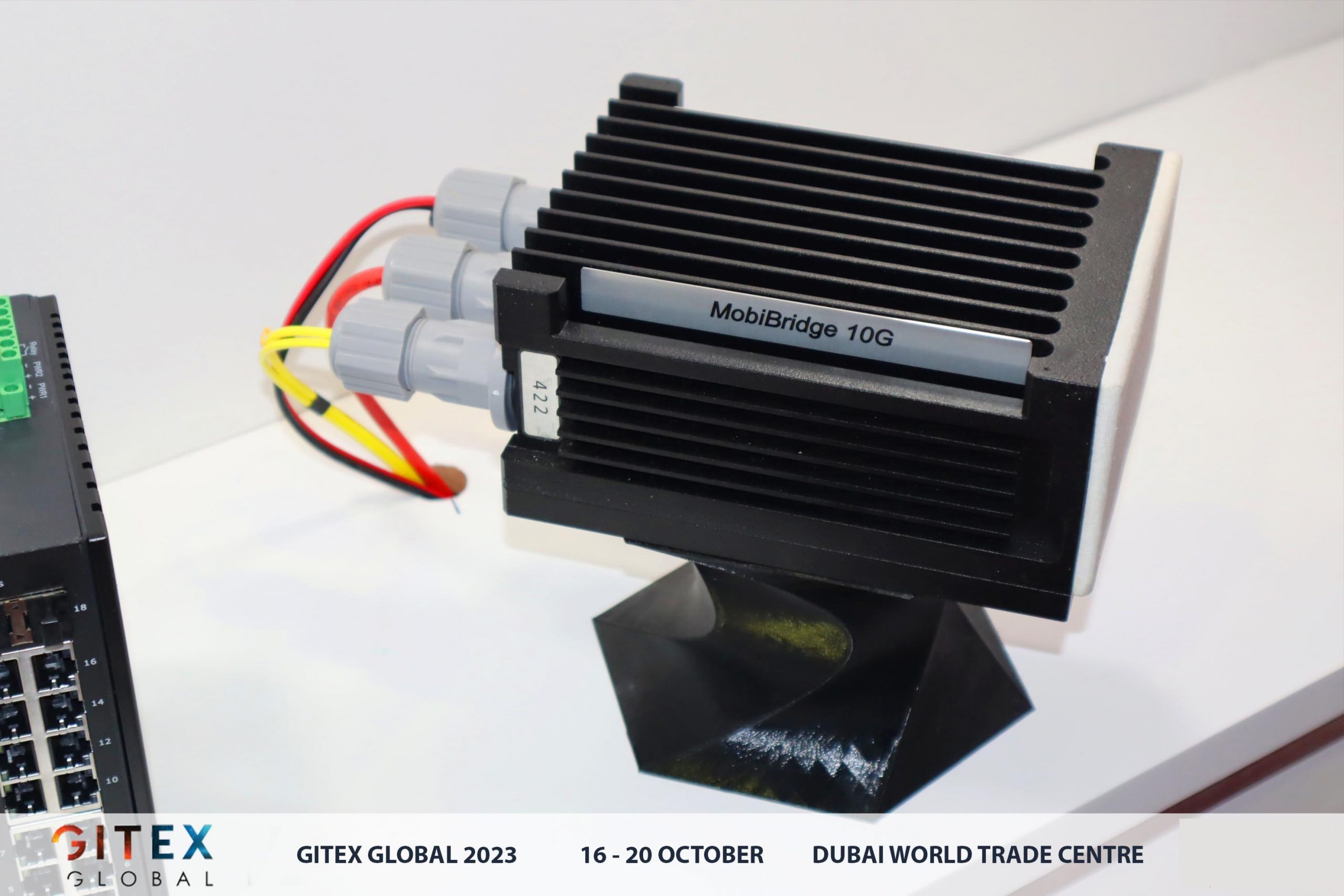
Exciting news from ELVA-1 as they unveil the upgraded 10 Gbps MobiBridge-10G Black Edition radio link, revolutionizing high-speed data transmission. Operating within the V-band spectrum, specifically in the license-free 57-71 GHz range, this cutting-edge radio link opens up a world of possibilities for seamless communication.
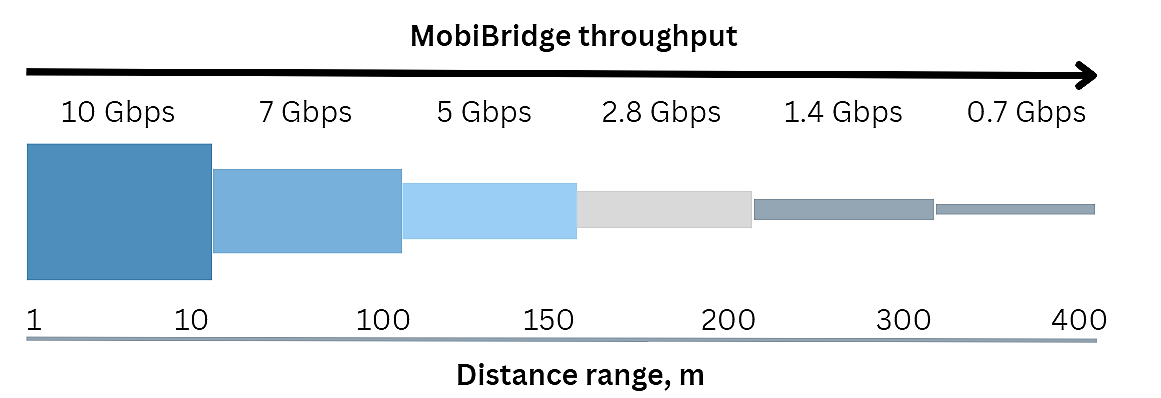
The MobiBridge-10G Black Edition boasts a maximum operational distance of 400 meters, ensuring reliable and lightning-fast connectivity. But what sets this radio link apart from others in the market? Let’s delve into the enhancements that make it a game-changer.
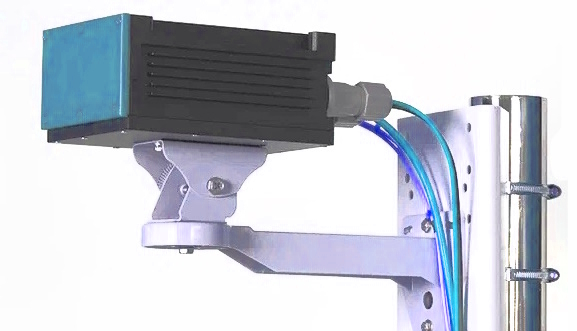
One notable improvement is the incorporation of a new dual degree of freedom bracket and an enhanced lower metal plate, ingeniously designed to optimize heat dissipation from the radio unit housing. This advancement not only ensures the longevity of the equipment but also boosts its performance in varying environments.
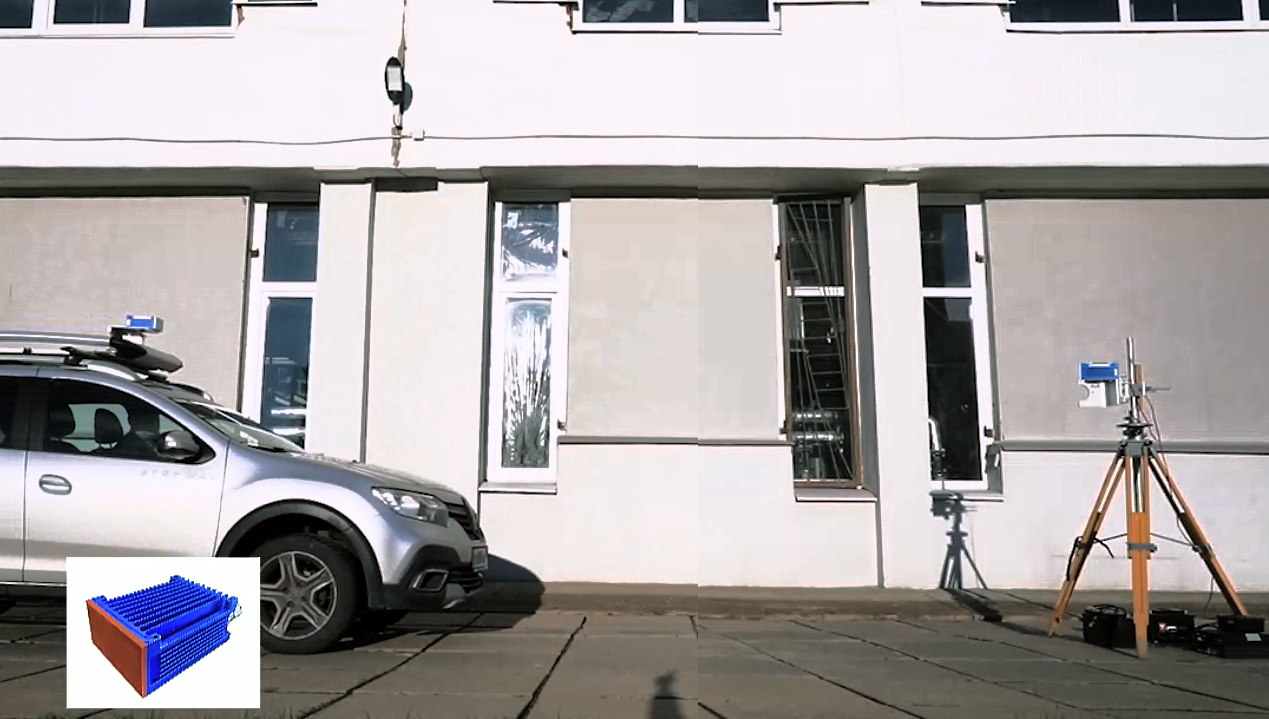
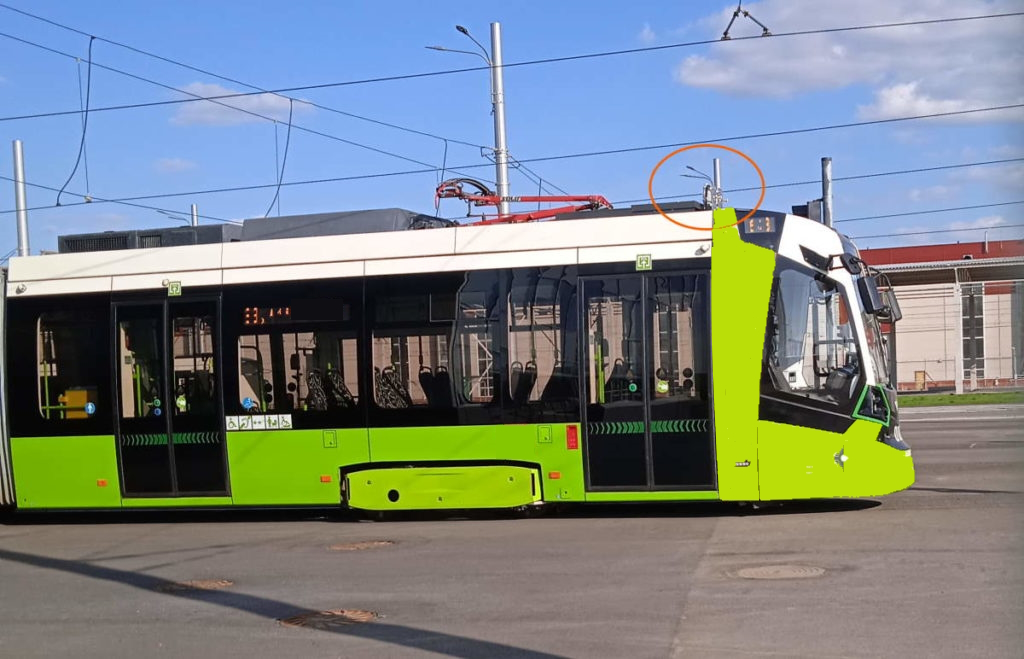
Moreover, the new bracket facilitates effortless mounting of the MobiBridge-10G radio on vertical supports. This user-friendly feature makes it ideal for applications in streetcar depots and bus terminals, enabling seamless communication with vehicles and enhancing overall transportation efficiency.
However, the true versatility of the MobiBridge-10G radio link lies in its applications in seaports, where it connects cruise ships and ferries to a vast number of passengers with high-speed broadband Internet. Seamlessly integrating with the port IT infrastructure, this radio link enhances the onboard experience and brings a new level of connectivity to the maritime industry.
But why is the V-band spectrum the perfect choice for this revolutionary technology? The answer lies in its license-free nature and ease of use. Unlike other frequency bands, the V-band does not require users to obtain expensive licenses, significantly reducing the deployment costs and eliminating bureaucratic hurdles. This makes it an attractive option for businesses and organizations seeking cost-effective solutions for high-speed data communication.
Additionally, the V-band offers a wide spectrum availability, which translates into reduced interference and enhanced signal quality. Users can enjoy a reliable and stable connection, making it perfect for critical applications such as communication with crewless vessels, data downloading, and software updates for onboard technical systems.
In conclusion, the 10 Gbps MobiBridge-10G Black Edition radio link by ELVA-1 is a groundbreaking innovation that brings high-speed connectivity to various sectors. With its optimized performance, user-friendly design, and seamless integration into different applications, it is set to transform the way we communicate and connect in the modern world. And with the V-band’s license-free nature and ease of use, this technology becomes an accessible and cost-effective solution for businesses and industries looking to embrace the future of data transmission.